The model that describes how data is written to a blockchain is known as the consensus mechanism. Consensus mechanisms determine how transactions are validated and added to the blockchain.
It plays a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of the network. Blockchain technology has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential to revolutionize various industries. At its core, the blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
Understanding how data is written to a blockchain is essential for grasping its functionality and potential applications. This article provides insights into the model that governs the process of writing data to a blockchain and its significance in the context of decentralized digital systems.
Blockchain Basics
The key model for writing data to a blockchain is called “Proof of Work”.
Blockchains are decentralized ledgers that store records in a sequence of blocks.
Each block contains a group of transactions that are added to the chain.
Transaction data is encrypted using cryptographic techniques for security.
Miners validate transactions and add blocks by solving complex algorithms.
Once a block is added, it is difficult to alter previous blocks, ensuring data integrity.
This process creates a transparent and trustless system for storing information.
Blockchain technology has applications beyond cryptocurrencies, such as smart contracts and supply chain management.
Data Writing In A Blockchain
The process of the data writing in a blockchain follows a specific model that dictates how information is stored securely. Each transaction is added to a block, which is then linked to the previous block, creating an immutable chain of data records.
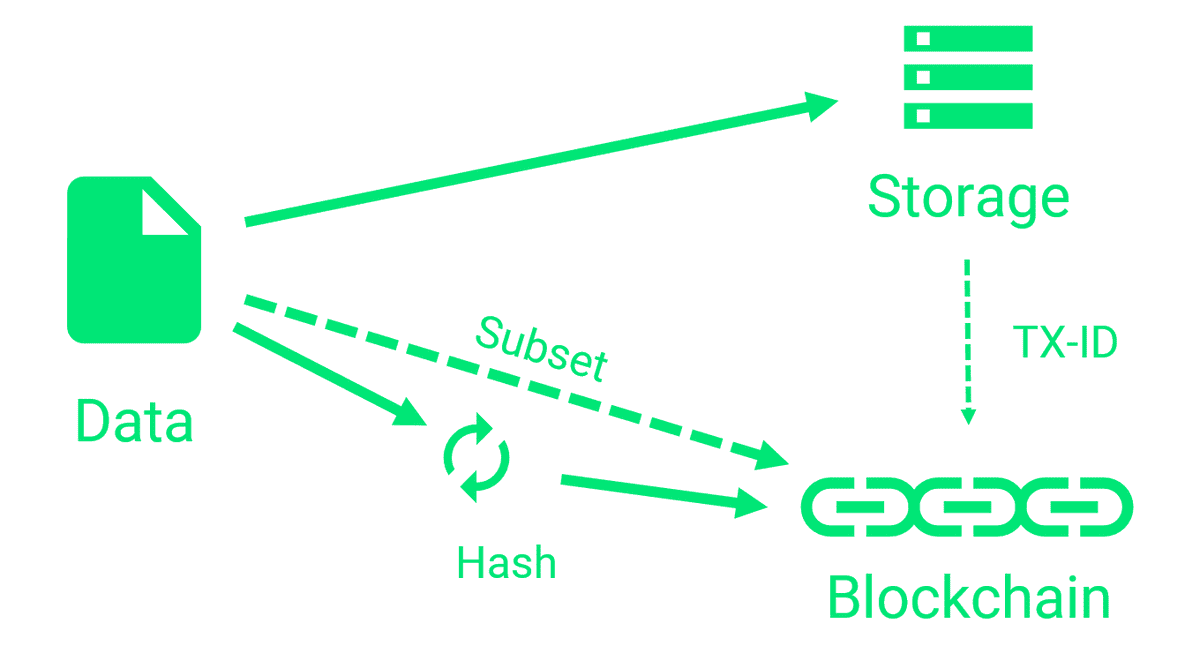
This structured approach ensures transparency and integrity in the blockchain network.
| Understanding the importance of data writing |
| Data writing in a blockchain is crucial for ensuring accuracy and security. |
| The role of transactions |
| Transactions play a key role in recording data changes on a blockchain ledger. |
| Different models for data writing |
| Various models determine how data is written to a blockchain, such as UTXO and account-based models. |
Model 1: Proof Of Work (PoW)
Overview of PoW: Proof of Work (PoW) is a popular consensus algorithm used in blockchain technology to secure and validate transactions. It involves miners solving complex mathematical puzzles to add new blocks of transactions to the blockchain.
How data is written using PoW: In a PoW system, when a transaction is made, it is broadcasted to the network and included in a block. Miners then compete to solve the mathematical puzzle associated with the block. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to append the block to the blockchain, and the transactions within the block are considered confirmed.
Advantages and disadvantages: One advantage of PoW is its strong security, as it requires significant computational power to alter past transactions. However, PoW is energy-intensive and can lead to high transaction fees. It also favors miners with more computing power, potentially centralizing control in the hands of a few. Moreover, the computational resources required for mining can contribute to environmental concerns.
Model 2: Proof Of Stake (PoS)
Proof of stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism used in blockchain networks to validate and create new blocks. In PoS, block validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
Overview of PoS:
Unlike proof of work (PoW), PoS block creators are selected deterministically, minimizing the need for computational power.
How data is written using PoS:
Data is written to a blockchain using PoS by validating transactions and creating new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency staked.
Advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of PoS include energy efficiency and reduced power consumption. However, it may lead to centralization if a few participants hold a significant amount of coins.
Model 3: Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS)
Overview of DPoS: DPoS is a consensus algorithm that requires coin holders to vote for delegates who maintain the blockchain. How data is written using DPoS: In DPoS, a small group of delegates is responsible for validating transactions and creating blocks. Advantages: DPoS is faster and more scalable than other models, as well as more energy-efficient. It also offers a more democratic and decentralized approach to block production. Disadvantages: Some argue that DPoS is more centralized, and there is a risk of voter apathy and cartel formation among delegates.
Model 4: Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
Overview of PBFT:
PBFT is a consensus algorithm designed for blockchain networks where the number of participating nodes is known and the trust among these nodes is established. In this model, a leader node is designated to handle the consensus process. PBFT divides the overall transaction processing into multiple phases, including a request phase, pre-prepare phase, prepare phase, and commit phase. This ensures that all the nodes in the network agree on the order of transactions.
How data is written using PBFT:
When a client sends a request to write data to the blockchain, the leader node acknowledges the request and broadcasts it to all other nodes. The nodes then validate the request, and if a consensus is reached, they execute and commit the request. This ensures that the same data is written to all the nodes in the network.
Advantages and disadvantages:
PBFT offers several benefits, including high speed and scalability, as it can handle a large number of transactions per second. It also ensures safety and consistency in the network. However, PBFT has some drawbacks. It requires a known and trusted set of nodes in the network, which limits its applicability to private or permissioned blockchains. Additionally, PBFT is more resource-intensive compared to other consensus algorithms, as it requires constant communication and message exchange among the nodes.
Frequently Asked Questions For Which Model Describes How Data Is Written To A Blockchain
What Is The Role Of A Consensus Algorithm In Blockchain Data Writing?
The consensus algorithm determines how data is approved and added to the blockchain, ensuring agreement among network participants.
How Does The Proof Of Work Model Contribute To Data Writing On A Blockchain?
Proof of Work involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate and add transactions to the blockchain, creating a secure and tamper-resistant system.
Why Is The Proof Of Stake Method Significant For Writing Data Onto A Blockchain?
With Proof of Stake, transactions are validated and added to the blockchain based on the stake or ownership of cryptocurrency, providing a more energy-efficient approach.
Conclusion
To summarize, understanding the model that describes how data is written to a blockchain is crucial in comprehending its functionality. The information presented in this blog post sheds light on the various models such as the UTXO model, account-based model, and DAG model.
Each model has its own strengths and weaknesses, catering to different blockchain use cases. Grasping these models will empower individuals to make informed decisions when navigating the complex world of blockchain technology.

