Cryptocurrency is recorded in financial accounting by adding digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum to the balance sheet at their market value when purchased, reflecting as a debit on the assets account. Common digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum are treated as intangible assets, initially recorded at cost and adjusted later by subtracting amortization over time and losses due to value drops.
Any increase in value after a drop is considered income. Accounting for cryptocurrencies involves recording values at the time of receipt and sale, similar to stock trading activities. One must record cryptocurrency transactions carefully using the correct journal entry, which is a debit to intangible assets-cryptocurrencies and a credit to other income in profit or loss.
Cryptocurrency is an innovative financial system that has created a new dimension in the accounting industry, providing diverse opportunities for businesses to adapt and evolve to the digital age.
Accounting For Cryptocurrency Transactions
Cryptocurrency transactions should be recorded similarly to stock trading activities. When digital assets like Bitcoin or Ether are purchased, they can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date of purchase. This will reflect as a debit on the assets account. Cryptocurrencies are often classified as intangible assets on financial statements. They are initially recorded at cost, which is the price they were bought for. Later on, their value is adjusted by subtracting amortization over time and losses due to value drops. Any increase in value after a drop is considered income. The accounting entry for cryptocurrencies involves debiting the intangible assets-cryptocurrencies account and crediting other income in profit or loss.
| Subheading | Link |
|---|---|
| Accounting for Cryptocurrencies – IFRS framework | https://frv.kpmg.us/reference-library/accounting-and-reporting-for-crypto-intangible-assets.html |
| How to Handle Crypto Trading Gains and Losses on Your Balance Sheet | https://cointelegraph.com/news/crypto-trading-gains-and-losses-how-to-handle-them-on-your-taxes |
| How to Account for Cryptocurrencies in Line with IFRS | https://www.cpdbox.com/accounting-cryptocurrencies-ifrs/ |
Challenges In Accounting For Cryptocurrencies
Accounting for cryptocurrencies presents several challenges due to their complex and rapidly changing nature. Cryptocurrency trading activities are recorded similarly to stock trading activities, and they should be classified and reported correctly on financial statements. Proper accounting practices require recording the fair market value of digital assets on the date they were acquired and calculating any gains or losses in value over time.
Cryptocurrency trading activities are recorded in accounting similar to those of stock trading activities. If an individual purchases Bitcoin or Ether, these digital assets can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date of purchase, reflecting as a debit on their assets account. However, there are challenges in accounting for cryptocurrencies. One challenge is the price volatility of cryptocurrencies, affecting the fair value of the assets.
Another challenge is the lack of consensus on reporting standards, making it difficult to compare financial statements across different organizations. Despite these challenges, accounting for cryptocurrencies can be done by treating them as intangible assets, initially recorded at cost and later adjusted by subtracting amortization and losses due to value drops, with any increase in value after a drop considered as income. Therefore, it is crucial to record the value of cryptocurrency accurately in financial statements.
Cryptocurrency Accounting Under IFRS And US GAAP
Cryptocurrency is treated as an intangible asset under the US GAAP framework and can be added to a balance sheet at its fair market value on the date of purchase. Crypto trading activities can be recorded similarly to stock trading activities, resulting in a debit on the assets account.
The accounting entry for cryptocurrency is to debit intangible assets and credit other income in profit or loss.
| Classification of Cryptocurrencies under IFRS and US GAAP: |
| Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ether, are often classified as intangible assets under US GAAP, while IFRS does not specifically address their classification. |
| Treatment of Cryptocurrencies in Financial Statements under IFRS and US GAAP: |
| Under IFRS and US GAAP, cryptocurrencies are initially recorded at cost and are adjusted for amortization over time as well as losses due to value drops. Any increase in value after a drop is considered income. Cryptocurrency trading activities are recorded similarly to stock trading activities. |
Cryptocurrencies have gained considerable attention in the financial world due to their growing popularity. The classification of cryptocurrencies under IFRS and US GAAP differs, with US GAAP treating cryptocurrencies as intangible assets. However, both accounting standards mandate that cryptocurrencies be initially recorded at cost. This is followed by regular adjustments for losses due to value drops and amortization over the period of use. Any increase in value after a drop in value is considered as income. Cryptocurrency trading activities should be recorded similarly to stock trading activities, with the fair market value of the digital assets reflecting as a debit on assets account in the balance sheet.

Best Practices In Cryptocurrency Accounting
Cryptocurrency usage in financial accounting involves recording digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum as intangible assets at their fair market value during purchase. Trading gains and losses are recorded similarly to stock trading activities, and there are specific accounting guidelines for cryptocurrencies under US GAAP framework and IFRS.
The most significant accounting practice for digital assets is to record their value at the time of receiving.
Cryptocurrency transactions should be recorded similarly to stock trading activities. Buying Bitcoin or Ether should be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date of purchase. This will reflect as a debit on the assets account. It is important to hire experienced professionals who understand cryptocurrency accounting regulations. Regularly reviewing and updating policies ensures all changes and updates are being made in a timely manner.
Adopting robust cryptocurrency reporting tools can help regulate and streamline the accounting process. Cryptocurrencies are initially recorded at cost and adjusted with amortization and value drops. Any increase in value after a drop is considered income. It is crucial to classify cryptocurrencies under US GAAP as intangible assets. By following these practices, businesses can ensure they are accurately accounting for their cryptocurrency transactions.
Understanding Tax Implications On Cryptocurrency Transactions
Accounting for cryptocurrency transactions is a complex process that involves properly recording the transactions in financial statements. Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ether, are commonly accounted for as intangible assets and should be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date of purchase.
This will reflect as a debit on the assets account. Understanding the tax implications on cryptocurrency transactions is crucial for businesses that use it in financial accounting.
Cryptocurrency trading should be treated similar to stock trading in accounting. For instance, Bitcoin or Ether can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the day they were bought, reflecting a debit to the assets account. One must classify cryptocurrencies as intangible assets initially recorded at cost when it comes to financial statements, and their value should be adjusted by subtracting amortization and losses due to value drops.
Any increase in value after a drop counts as income. Cryptocurrency transactions have tax implications, including taxable events such as capital gains tax. It’s important to keep accurate records of cryptocurrency trading gains and losses on your balance sheet and be aware of tax implications as per the current laws of your country. By following these guidelines, businesses can successfully manage and account for cryptocurrency in their financial accounting.
Future Of Cryptocurrency Accounting
The development of cryptocurrency-specific reporting standards is crucial for the future of cryptocurrency accounting. With the increased adoption of cryptocurrencies in mainstream finance, it is important to have standardized reporting guidelines to ensure transparency and accuracy in financial reporting.
Cryptocurrency trading activities should be recorded similarly to those of stock trading activities. If one buys Bitcoin (BTC) or Ether (ETH), these digital assets can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date the assets were purchased. This will reflect as a debit on one’s assets account, and the journal entry is: Debit Intangible assets – cryptocurrencies; Credit Other income in profit or loss. It is also important to classify cryptocurrencies correctly on financial statements. Many of the most common digital assets, like bitcoin, ether, solana, or cardano, are accounted for as intangible assets under US GAAP (crypto intangible assets).
Furthermore, cryptocurrency as intangible assets are initially recorded at cost (i.e., the price they were bought for). Later on, their value is adjusted by subtracting amortization over time (if any) and losses due to value drops. Finally, any increase in value after a drop is considered income. Accounting for cryptocurrency and digital assets is still evolving, but it is crucial for businesses and investors to properly account for these assets to make informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions On How Is Cryptocurrency Used In Financial Accounting
How Is Cryptocurrency Treated In Accounting?
Cryptocurrency trading activities are recorded similarly to stock trading activities in accounting. Bitcoin or Ether purchased can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date it was purchased. Cryptocurrencies are accounted for as intangible assets, initially recorded at cost and adjusted for amortization and losses due to value drops.
Any increase in value after a drop is considered income. A journal entry is made by debiting Intangible assets – cryptocurrencies and crediting Other income in profit or loss.
How Do You Record Cryptocurrency Transactions In Accounting?
To record cryptocurrency transactions in accounting, treat them like stock trades. When purchasing digital assets like Bitcoin or Ether, add them to the balance sheet at their fair market value. This reflects as a debit on the assets account. Cryptocurrencies are often classified as intangible assets.
The typical accounting entry is to debit intangible assets – cryptocurrencies and credit other income in profit or loss.
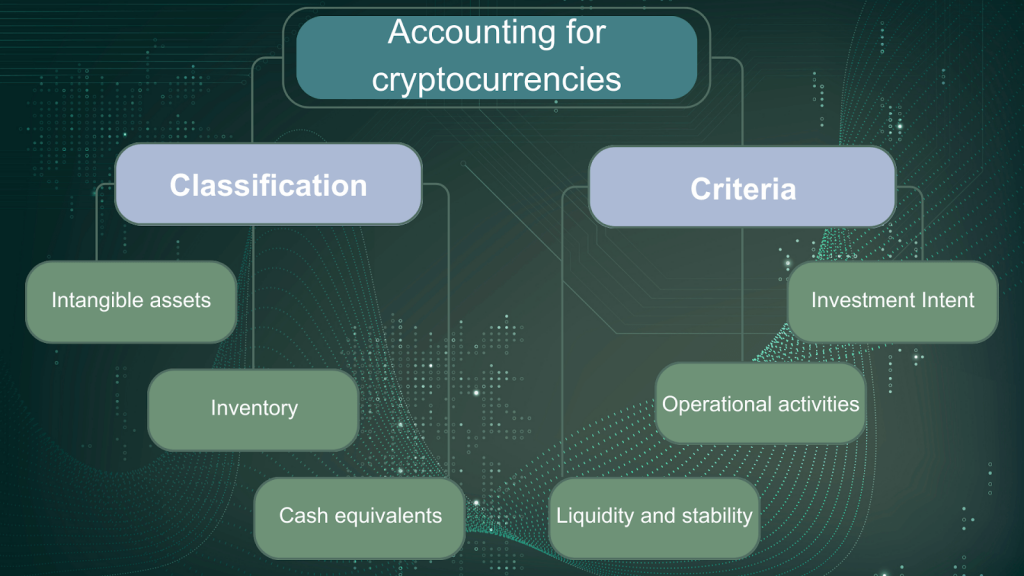
How Should Cryptocurrencies Be Classified On The Financial Statements?
Cryptocurrencies should be classified as intangible assets in financial statements. The digital assets can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value on the date of purchase, reflecting as a debit on one’s assets account. Any increase or decrease in value over time due to losses or amortization should be adjusted accordingly.
What Is The Accounting Entry For Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency transactions are recorded similarly to stock trading activities. If you buy Bitcoin or Ether, the digital assets can be added to the balance sheet at their fair market value, reflecting a debit on the assets account. Cryptocurrencies are classified as intangible assets under US GAAP and should be initially recorded at cost and later adjusted for value drops or increases.
The accounting entry for cryptocurrency is a Debit to Intangible Assets-Cryptocurrencies and a Credit to Other Income in profit or loss.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency is becoming a popular form of investment that is now being recognized by financial accounting. Its classification as intangible assets under US GAAP enables businesses to record transactions as they would for stock trading activities. Though there are still grey areas and challenges to overcome in accounting for cryptocurrencies, it is evident that it is slowly taking its rightful place in financial accounting.
It is crucial for businesses to stay updated with the latest developments to ensure compliance with accounting regulations.

