Bitcoin transactions involve sender, receiver, digital signatures, and verification by miners on the blockchain network. To understand how Bitcoin transactions work, it is essential to grasp the key elements behind the process.
In simple terms, a sender initiates a transaction by signing it with their private key, which is then verified by network nodes. Upon verification, the transaction is added to a block and added to the blockchain through a consensus mechanism known as mining.
Miners confirm the legitimacy of the transaction and add it to the public ledger for transparency and security. This decentralized system ensures the smooth functioning of Bitcoin transactions while maintaining the integrity of the network.
An Introduction To Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates on a decentralized network using blockchain technology. It allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks. The rise of Bitcoin has gained significant attention due to its potential for disrupting traditional financial systems. It has a limited supply of 21 million coins, which adds to its value. Bitcoin transactions involve sending and receiving coins through digital wallets using cryptographic keys. These transactions are verified and added to the blockchain through a process called mining. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and secure the network. This process ensures transparency and security within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
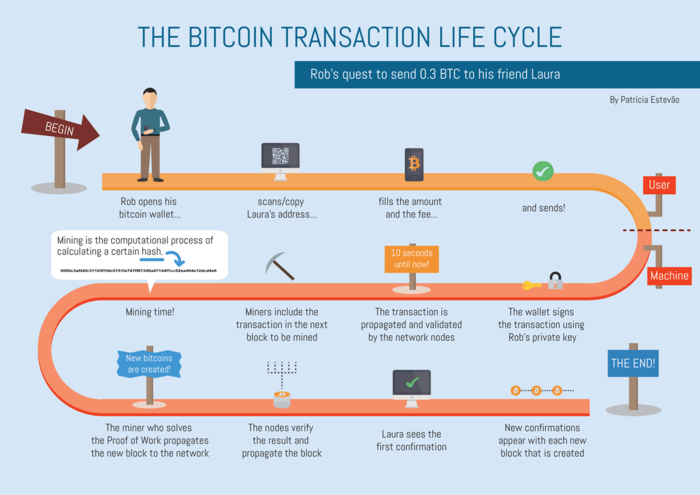
Bitcoin Transactions Explained
Bitcoin Transactions Explained
What is a Bitcoin Transaction?
How Do Bitcoin Transactions?
Bitcoin transactions involve sending or receiving bitcoins between digital wallets. Each transaction gets recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. When a transaction is initiated, it goes through a process called mining. Miners verify the transaction and add it to a block, which then becomes part of the blockchain. This process ensures that transactions are secure and cannot be tampered with. Once a transaction is confirmed, the bitcoins are transferred from one wallet to another. Bitcoin transactions operate on a decentralized network, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks, making them fast, secure, and cost-effective.
The Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin transactions are processed through a decentralized network. Each transaction is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain. This ledger is secure and transparent, ensuring that transactions cannot be altered fraudulently. The blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to maintain the integrity of the data. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in chronological order, creating a secure and immutable record of transactions.
Step-by-step Process Of A Bitcoin Transaction
Creating a Bitcoin Wallet: To start with a Bitcoin transaction, one needs a digital wallet, which can be obtained through various online platforms.
Generating a Bitcoin Address: Once the wallet is set up, it will generate a unique Bitcoin address to send and receive funds.
Initiating a Transaction: When sending Bitcoin, the sender enters the recipient’s address and the amount to be sent, followed by a digital signature for security.
Verifying the Transaction: The network validates the transaction to ensure that the sender has sufficient funds and confirms the authenticity of the digital signature.
Adding the Transaction to the Blockchain: Lastly, the verified transaction is added to a block, which is then added to the blockchain, making the transaction irreversible and publicly recorded.
Transaction Fees And Confirmation Times
Bitcoin transactions work through a decentralized network of computers known as the blockchain. When a user initiates a transaction, it is added to a pool of unconfirmed transactions. Miners then compete to validate these transactions by solving complex mathematical puzzles.
Transaction fees are paid by users to incentivize miners to include their transaction in the next block. These fees are determined by various factors, including the current network congestion and the size of the transaction in bytes.
The factors affecting transaction fees include the transaction size, the priority assigned to the transaction, and the current network congestion. Transactions with higher fees are usually prioritized and confirmed more quickly.
Confirmation times refer to the time it takes for a transaction to be included in a block and added to the blockchain. This can vary depending on the network congestion and the fee paid. Block confirmations represent the number of blocks that have been added to the blockchain since the transaction was included.
Overall, transaction fees and confirmation times are important considerations for Bitcoin users, as they can impact the speed and cost of transactions on the network.
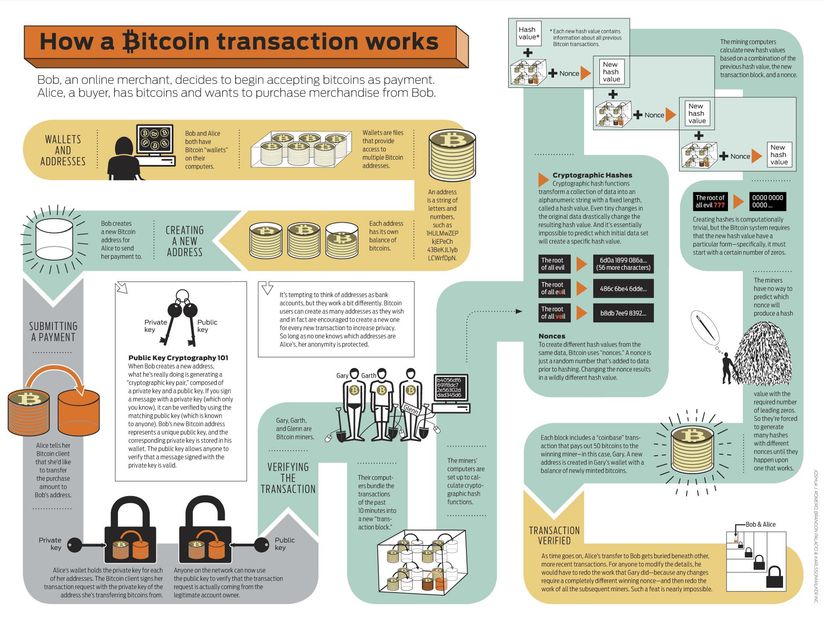
Types Of Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions work through a decentralized system called the blockchain. This technology ensures the transparency and security of the transactions. There are different types of Bitcoin transactions:
Standard transactions are the most common type where one person sends Bitcoin to another.
Multisignature transactions require multiple signatures to authorize a transaction, which adds an extra layer of security.
| Type of Transaction | Description |
|---|---|
| Standard Transactions | Most common. One person sends Bitcoin to another. |
| Multisignature Transactions | Multiple signatures needed to authorize a transaction. |
| Segregated Witness (SegWit) Transactions | Optimizes transaction data storage, allowing more transactions per block. |
Segregated Witness (SegWit) transactions optimize the storage of transaction data, enabling more transactions per block and reducing fees. This innovation has helped address scalability issues.
Understanding the different types of Bitcoin transactions is essential for safely and efficiently participating in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The Role Of Miners
Miners play a crucial role in the Bitcoin transaction process. They are responsible for verifying and adding transactions to the Blockchain by solving complex mathematical algorithms.
The mining process involves the use of high-powered computers to solve these cryptographic puzzles in order to validate transactions.
Upon successful validation, miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins as well as the transaction fees associated with the verified transactions.
The Future Of Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions operate through a decentralized network of computers. Each transaction involves sending and receiving digital assets. Scaling solutions like the Lightning Network aim to improve transaction speed. This technology enables faster and more scalable transactions. By implementing these improvements, Bitcoin can potentially handle more transactions. Overall, advancements in transaction speed and scalability are crucial for the future of Bitcoin transactions.

Frequently Asked Questions Of How Do Bitcoin Transactions Work
How Are Bitcoin Transactions Verified?
Bitcoin transactions are verified through a process called mining. Miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. This ensures that only legitimate transactions are recorded and prevents fraud or double-spending.
Can Bitcoin Transactions Be Traced?
Yes, Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the blockchain, which is a public ledger. While the transactions are pseudonymous, meaning they don’t reveal personal information, it is still possible to trace them back to specific addresses. However, with the right precautions, Bitcoin transactions can be made more privacy-focused.
How Long Does A Bitcoin Transaction Take?
The time it takes for a Bitcoin transaction to be confirmed can vary. On average, it takes around 10 minutes for a transaction to receive the first confirmation. However, during times of high network congestion, it can take longer. To speed up transactions, users can include a higher transaction fee.
Are Bitcoin Transactions Reversible?
Bitcoin transactions are generally irreversible. Once a transaction is included in a block and confirmed by the network, it is very difficult to reverse. This immutability is one of the key characteristics of Bitcoin and provides security and trust in the system.
However, it is recommended to only transact with trusted parties.
Conclusion
In understanding Bitcoin transactions, it’s clear that the blockchain technology offers secure, transparent, and decentralized processes. With its potential to revolutionize financial systems, Bitcoin is gaining traction globally. As the world continues to embrace digital currencies, it’s essential to grasp the intricacies of this innovative payment system.

