Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. It allows for decentralized and transparent transaction tracking.
Blockchain technology revolutionizes traditional data management by distributing copies of the ledger to all network participants, ensuring trust and security. Blockchain technology has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to transform various industries. By providing a decentralized ledger system, blockchain ensures secure and transparent transaction records.
Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, blockchain distributes copies of the ledger to all participants, promoting trust and eliminating the need for intermediaries. This innovative technology has the power to enhance data integrity, prevent fraud, and optimize processes across businesses globally. In this digital age, understanding how blockchain works and its advantages is essential for staying relevant and competitive in today’s rapidly evolving market landscape.
What Is Blockchain?
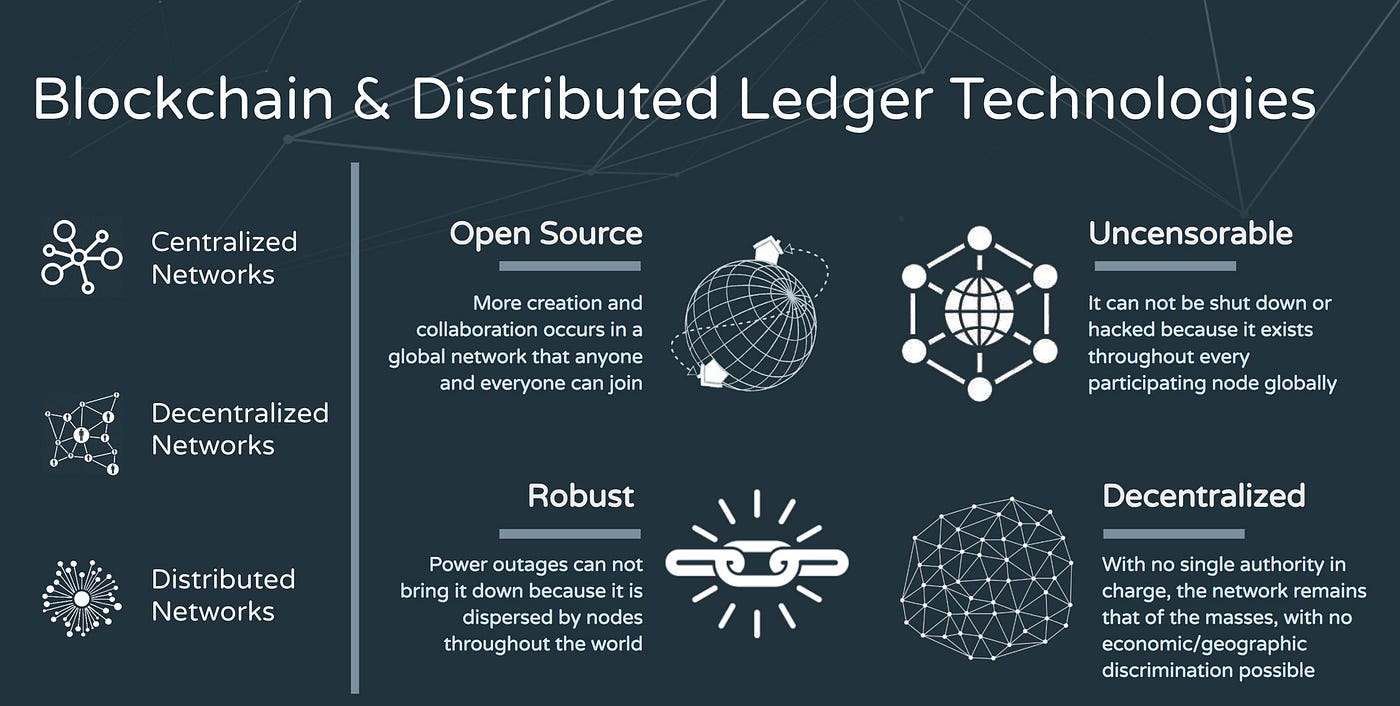
Blockchain is a method of recording information that makes it impossible or difficult for the system to be changed, hacked, or manipulated. It is a distributed ledger that duplicates and distributes transactions across the network of computers participating in the blockchain.
There are two major types of blockchains: public and private. Public blockchains offer more accessibility, innovation, security, and transparency, while private blockchains provide more control and privacy.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Blockchain Vs. Traditional Ledgers
Blockchain vs. Traditional Ledgers
A blockchain is a well-known example of distributed ledger technology. It differs from traditional ledgers as a copy of the ledger is distributed to each node in the network. This allows every node to view, modify, and verify the ledger, ensuring trust and transparency. There are two major types of blockchains: public and private. Public blockchains offer more accessibility, innovation, security, and transparency, whereas private blockchains provide more control and privacy.
Difference between blockchain and bank ledger
Data on the blockchain is immutable, tamper-proof, and can keep track of all transactions without the fear of being altered or deleted. On the other hand, banking ledgers can be edited, deleted, and modified, making them reversible. A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records securely linked together via cryptographic hashes.

Frequently Asked Questions Of Blockchain Is A Ledger
Is A Blockchain A Centralized Ledger?
No, a blockchain is not a centralized ledger. It is a distributed ledger technology where a copy of the ledger is distributed to each network node, allowing every node to view, modify, and verify the ledger for trust and transparency.
Is Blockchain A Private Ledger?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger where all network nodes can view, modify, and verify transactions, ensuring trust and transparency.
What Is The Blockchain In Simple Terms?
Blockchain is a method of recording information that is secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering. It is a distributed ledger that duplicates and distributes transactions across a network of computers, ensuring trust and transparency.
What Is The Difference Between A Bank Ledger And A Blockchain?
A bank ledger can be edited, deleted, and reversed. Data on blockchain is immutable, cannot be tampered with, and ensures transparency and trust.
Conclusion
Blockchain is revolutionizing the way we keep records and ensuring trust and transparency in transactions. Unlike traditional ledgers, blockchain is a distributed ledger technology where every node on the network can view, modify, and verify the ledger. This decentralized system provides security and immutability, making it difficult for the system to be hacked or manipulated.
Whether it’s public or private, blockchain offers accessibility, innovation, and transparency, or control and privacy. Embracing blockchain technology opens up a world of possibilities, enabling secure and efficient transactions across various industries.

